You’ve probably heard the term ‘grassroots activism’ thrown around in political conversations or across news headlines, but what does it truly signify? Essentially, grassroots activism encapsulates the power and passion of ordinary people making an extraordinary impact. Fueled by their deep commitment to bringing about change, these activists challenge the status quo, inspire communities, and spark social transformation. In this comprehensive expose, we will explore ten textbook examples of grassroots activism that have carved a niche in the annals of history.
1. The Civil Rights Movement

The Civil Rights Movement was a pivotal grassroots movement that swept across the United States from the mid-1950s into the late 1960s. Primarily led by African Americans, the movement was a struggle against the rampant racial discrimination and segregation that pervaded every aspect of life. The fight was not just for equal rights under the law but also for recognition and respect as human beings.
One particular incident that triggered the grassroots momentum was Rosa Parks’ refusal to give up her bus seat to a white man in Montgomery, Alabama, in 1955. This act of civil disobedience led to the Montgomery Bus Boycott, a year-long protest that resulted in the U.S. Supreme Court ruling segregation on public buses unconstitutional. The boycott also introduced a young Martin Luther King Jr. to the nation, whose powerful oratory and principles of nonviolent resistance would shape the course of the civil rights movement.
2. The Anti-Apartheid Movement

The anti-apartheid movement in South Africa was a struggle against a brutal system of racial segregation and discrimination enforced by the white minority government. Ordinary people, particularly the black majority, risked their lives to fight the injustices imposed by the apartheid regime. The movement wasn’t confined to South Africa—it ignited global outrage, leading to international sanctions and boycotts that ultimately forced the South African government to negotiate an end to apartheid.
One pivotal grassroots campaign was the Soweto Uprising in 1976. Tens of thousands of black schoolchildren protested against the government’s decision to enforce Afrikaans, a language associated with oppression, as a medium of instruction in black schools. The brutal police response ignited further resistance, making Soweto a turning point in the anti-apartheid struggle. The Uprising shone a harsh global spotlight on the horrors of apartheid, precipitating its ultimate downfall.
3. The Women’s Suffrage Movement
The women’s suffrage movement was a decades-long fight for gender equality and women’s right to vote. Grassroots activists organized protests, signed petitions, and lobbied for their cause, challenging the deeply entrenched patriarchal norms of society. They faced mockery, imprisonment, and even violence in their quest for women’s suffrage.
The movement gradually gained momentum, with women in different parts of the world winning the right to vote at different times. In the United States, the 19th Amendment to the Constitution was ratified in 1920, finally granting American women the right to vote. This achievement marked a significant milestone in the long journey towards gender equality—a journey that still continues today.
4. The Gay Rights Movement – Stonewall Uprising

The fight for LGBT rights in the United States gained significant momentum with the Stonewall Uprising in 1969. It began as a reaction to a police raid on the Stonewall Inn, a gay bar in New York City. Patrons and neighborhood residents, frustrated with constant harassment and discrimination, resisted the raid, sparking a series of protests.
The Stonewall Uprising galvanized the LGBT community, leading to the formation of activist groups that championed the cause of gay rights. The incident was a catalyst for the global gay rights movement, giving birth to annual Pride marches and serving as a reminder of the continued struggle for LGBT acceptance and equality.
5. The Green Belt Movement
The Green Belt Movement was a grassroots environmental initiative launched in Kenya in 1977. Spearheaded by environmental activist Wangari Maathai, the movement aimed to combat the effects of deforestation, soil erosion, and water scarcity by planting trees across Kenya. Besides its ecological objectives, the movement also sought to empower rural communities, particularly women, by providing them with a source of income.
Over the years, the Green Belt Movement has resulted in the planting of over 51 million trees in Kenya, drastically altering the country’s landscape and significantly contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. The movement’s success lies in its ability to intertwine environmental conservation with socio-economic empowerment, a model that has been replicated across various parts of the world.
6. The Arab Spring
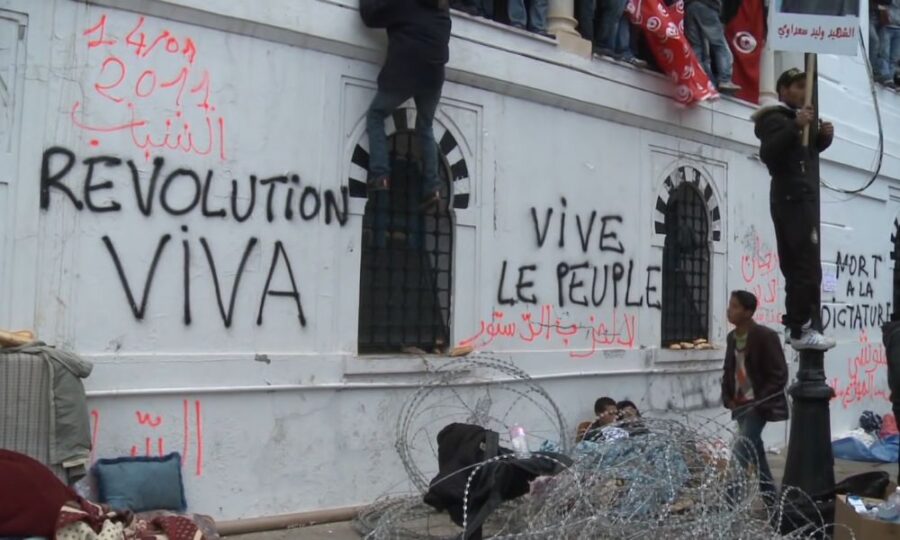

In 2010, a wave of protests, uprisings, and armed rebellions swept across the Middle East in what came to be known as the Arab Spring. It began in Tunisia when Mohamed Bouazizi, a street vendor, set himself on fire in protest against police corruption and a lack of economic opportunities. His act sparked nationwide protests, eventually leading to the ousting of President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali.
Bouazizi’s act of self-immolation ignited a wave of discontent that swept across the region. Ordinary citizens, empowered by social media, rose against long-standing authoritarian regimes in countries such as Egypt, Libya, and Yemen. While the outcomes varied from country to country, the Arab Spring represented an unprecedented display of grassroots activism in the region.
7. The Occupy Wall Street Movement
The Occupy Wall Street movement emerged in 2011 as a response to economic inequality and the perceived influence of corporations on government. It started with a small gathering in Zuccotti Park in New York City’s Wall Street financial district, protesting against what participants saw as the undue influence of corporations on democracy and the role of Wall Street in the financial crisis of 2007–2008.
The movement’s primary slogan, “We are the 99%,” referred to the growing income and wealth disparity in the U.S. between the wealthiest 1% and the rest of the population. The Occupy Wall Street movement spurred debates about economic inequality worldwide, and its grassroots tactics inspired similar protests in cities around the globe.
8. Black Lives Matter Movement
The Black Lives Matter movement emerged in 2013 following the acquittal of Trayvon Martin’s killer. The movement began as a hashtag, #BlackLivesMatter, on social media but quickly evolved into a global advocacy campaign against violence and systemic racism towards Black people. The grassroots campaign was led by three Black women: Alicia Garza, Patrisse Cullors, and Opal Tometi.
The movement gained renewed traction in 2020 following the murder of George Floyd. Protests broke out across the globe, pushing for police reform and highlighting the systemic discrimination faced by Black individuals. The Black Lives Matter movement continues to advocate for racial justice and equality, shaping conversations and policies on race relations in the U.S. and beyond.
9. #MeToo Movement

In 2017, the #MeToo movement emerged as a powerful campaign against sexual harassment and assault. Actress Alyssa Milano popularized the phrase when she encouraged victims to share their experiences on social media. The response was overwhelming, with millions of people, mostly women, coming forward with their stories.
The movement had a profound impact on society, exposing high-profile perpetrators and fostering a broader conversation about sexual harassment in the workplace. The #MeToo movement has since evolved into a global campaign, advocating for stronger laws and policies to combat sexual violence and harassment.
10. Fridays for Future
Fridays for Future is a global youth-led movement that began in 2018 when Swedish teenager Greta Thunberg started skipping school to protest outside the Swedish Parliament for stronger action on climate change. Her solitary protest soon garnered international attention, inspiring millions of students worldwide to join her in striking from school to demand action against climate change.
The Fridays for Future movement underscores the vital role of youth in driving social and environmental change. Despite their age, these young activists have managed to put pressure on governments and corporations to act responsibly towards the environment, demonstrating the power of grassroots activism in shaping the future of our planet.
Final Words
The narratives of grassroots activism are countless and diverse, reflecting the broad spectrum of human experiences. While we’ve covered some significant movements, this list is by no means exhaustive. Each example underscores the potential of ordinary people to instigate extraordinary change. Grassroots activism reminds us that every individual has the power to challenge injustices and shape their world—one step at a time. From civil rights to environmental justice, the legacy of grassroots activism continues to inspire us toward creating a better, more equitable world.

